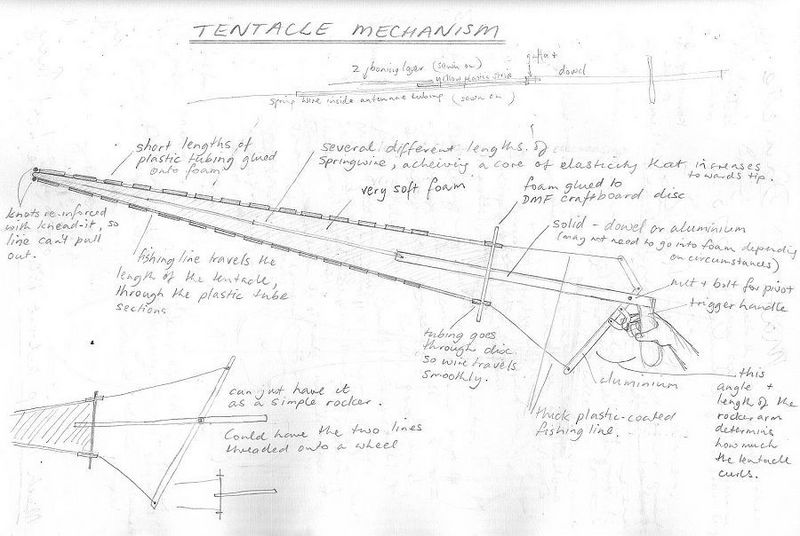
I’ve made a set of photos and notes that I took during Nori Sawa’s masterclass that I did at Unima 2008. Nori Sawa is a Japanese puppeteer, designer and maker who now works and teaches at the Academy of Performing Arts in Prague, and he taught us how to make a Ningyo-Joruri head. This is much the same as a traditional bunraku puppet head, having a neat neck mechanism and trigger in the handle so that the head has a smooth up-and-down action, which together with a shoulder plate that sits loosely locked around the neck (we didn’t have time to make this), gives the character a very flexible head and neck movement.
There were six of us doing the class (from Canberra, Melbourne, Hobart, Adelaide, Sydney and Alice Springs – how’s that for a good national spread?) and it went over the first 3 1/2 days of the festival. For me it proved a good way of learning some new skills and settling into the festival and getting to make some new friends, including Naomi Guss, whose blog I have been reading for some time now. It was good to finally meet her in person, and spend some time with her.
(Naomi and Nori, Kristen, Jill, Kathy, Frances and Vanessa (one of the organisers) – click to enlarge)
The making process involved sculpting a clay head; making a plaster mold; creating a hollow paper mache head by paper mache-ing inside the two halves of the mold and joining the resulting paper shells; shaping and joining the wood to make a handle, trigger and neck; stringing the trigger mechanism; and finally situating and attaching the neck into the head with an axle and elastic for return on the trigger. A lot to achieve in the time – we had a battle to get each stage dry and used hairdryers borrowed from our hotels, a microwave, the sun, and eventually a pie warmer to get there! I loved the moment when we sealed the two halves of the head together with white glue and a small red hot iron – it still seems magical to me that that works so well!
This is my puppet head in action. The clip is a little clumsy, since I was filming and operating, but it gives the idea. I haven’t decided what kind of finish to give it yet. I will at least paint the eyes.
Some aspects I don’t want to forget: The tradition in these puppets is for the chin to be prominent, and the focus of the puppeteer is on the chin, it leads the action. The eyes have a flat surface that is angled down; when the face lifts up you see the whole eye this way, and it lightens the whole character and mood. The action of the puppet and each movement it makes is that of a circle or infinity; this kind of choreography gives grace and life.
Sadly we didn’t get to see Nori perform because on the way to Australia his bag of puppets became one of the 16,ooo items lost at the choas of the shambles that is the new Heathrow Terminal 5. I’d love one day to see some of his contemporary puppets and shows that fuse Japanese and Czech design.
My attendence at Unima 2008 is supported by the ACT Government

























 These are two simple rod puppets which were made by my son when he was about 8, at a workshop that I was involved with.
These are two simple rod puppets which were made by my son when he was about 8, at a workshop that I was involved with.